Use of ozonated water as a new therapeutic approach to solve concerns around antitumour treatment
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine
Keywords: Ozone therapy, Drug resistance, Intratumoral oxygen partial pressure, intratumoral blood perfusion. cisplatin, ozonated water, tumor hypoxia.
Abstract
“Tumor hypoxia is a severe problem affecting tumor therapy because it reduces the sensitivity of chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Ozone has been known to improve peripheral blood perfusion and oxygen partial pressure. The effect of ozonated water on tumor hypoxia, alone and in combination with an antitumor drug was studied in the present study. ” (1)
“The present study showed that ozonated water increased intratumoral blood perfusion and improved tumor hypoxia. In addition, ozonated water increased the therapeutic effect of CDDP. These findings, as well as previous reports, suggest that tumor growth is suppressed after treatment with ozonated water as the amount of CDDP reaching the tumor is increased when the intratumoral blood perfusion is increased due to the ozonated water. Thus, the administration of ozonated water may be a new therapeutic approach to solve current concerns regarding antitumor treatment.” (1)
Introduction
Ozonated water is the liquid form generated when ozone is dissolved in saline, which is much easier to handle than the gaseous form. The safety and direct antitumor effect of ozonated water have been previously described by us (2).
The primary form of ozone therapy is major autohemotherapy (MAH). In MAH, patient blood is mixed with ozone gas before being retransfused. It has been known for its beneficial effects in cardiovascular diseases, infections, cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoarthritis (3).
Ozone gas is known to improve peripheral blood perfusion. Ozone therapy in tumor patients improves intratumoral oxygen partial pressure (3). Tumor hypoxia is a serious concern affecting tumor therapy because it reduces the sensitivity of chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Therefore, it is expected to improve the sensitivity of antitumor therapy. In clinical settings, the combination of radiation therapy and MAH or rectal administration of ozone gas/oxygen gas mixture has helped achieve the same effects as those obtained by using a combination of radiation therapy and chemotherapy in preventing the progression of head and neck cancer.
“Reports related to chemotherapy mostly discuss side effects; few reports discuss therapeutic effects. To the best of our knowledge, no other study has discussed ozone therapy using ozonated water. Therefore, a new approach using ozonated water was examined to solve concerns around antitumor treatment. In this report, we decided to study the effect of ozonated water on tumor hypoxia, alone and in combination with an antitumor drug.” (1)
Materials and Methods (Study)
Read Here
Results
Effect on blood gas and intratumoral oxygen partial pressure
Before and after the administration of O3 or sterile saline, no apparent change was noted in the blood gas levels (Table I). No significant difference was noted between the O3 and S groups.
In the S group, there was no apparent change in the intratumoral oxygen partial pressure. However, the partial pressure in the O3 group significantly increased compared to that in the S group at 20 min after administration (Fig. 1). It peaked at 50 min after administration and gradually decreased afterward. At 130 min after administration, no significant difference was noted between the O3 and S groups.
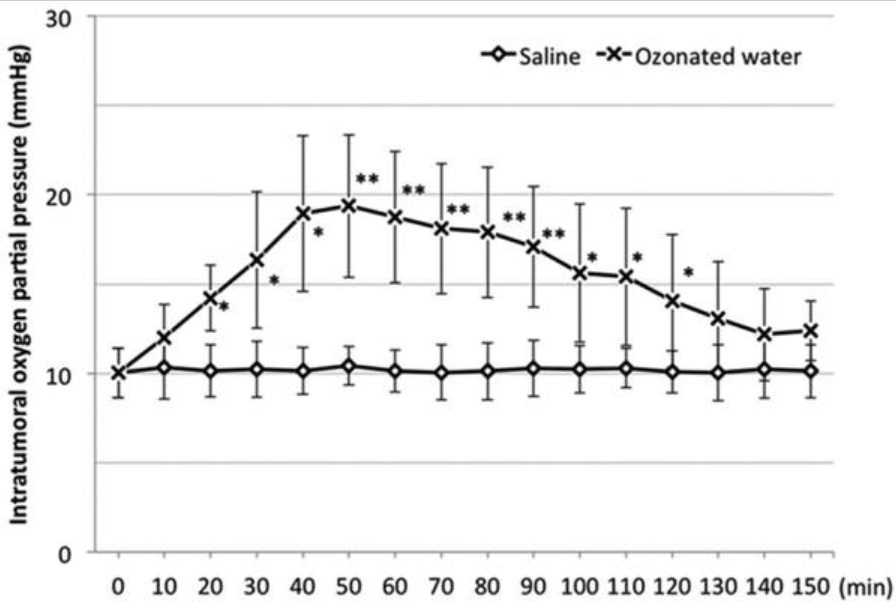
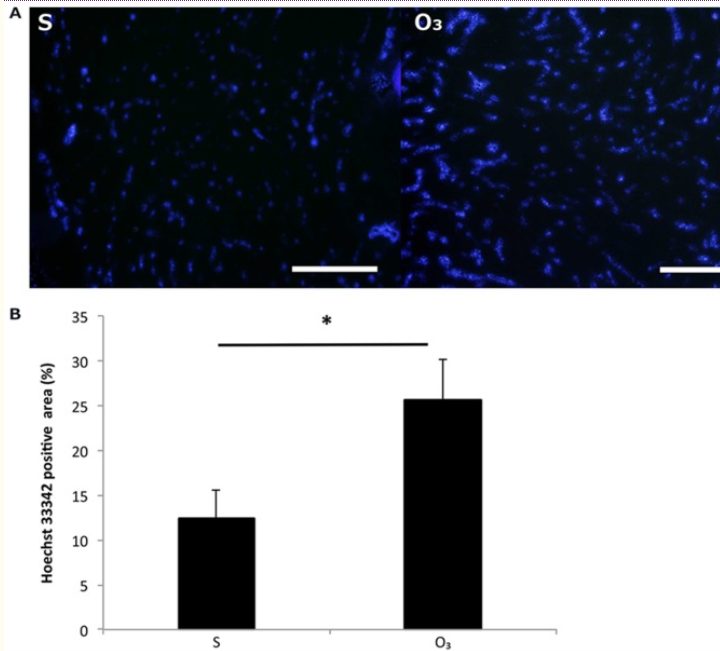
Effect on intratumoral blood perfusion
The intratumoral blood perfusion in the O3 group increased compared to that in the S group (Fig. 2). The H33342-positive area was 12.3±3.2{e43154ce913794517af217fcab284b44cfe906ba9a1c4ba2ecde5a9be0395ec5} in the S group and 25.6±4.6{e43154ce913794517af217fcab284b44cfe906ba9a1c4ba2ecde5a9be0395ec5} in the O3 group. There was a significant difference between the two groups (P<0.05).
Effect of ozonated water and cddp in combination
Tumor growth was significantly suppressed in the O3-CDDP5.0 group compared to that in the S and O3 groups (P<0.05) (Fig. 3). A statistically significant difference was not observed between the S-CDDP5.0 and O3-CDDP5.0 groups. However, tumor growth in the O3-CDDP5.0 group tended to be suppressed, compared to that in the S-CDDP5.0 group. In the O3-CDDP3.4 group, despite reducing the concentration of the antitumor drug, tumor growth suppression was observed, which was comparable to that observed in the S-CDDP group.

Read here for Figure 4 and Figure 5.
Brief Discussion
“The present study showed that ozonated water increases intratumoral blood perfusion and improves intratumoral oxygen partial pressure. In addition, tumor growth was more suppressed when ozonated water and CDDP therapy were combined. Thus, the administration of ozonated water could be a new approach to solve current concerns around antitumor treatment, such as tumor hypoxia and drug resistance of tumors.” (1)
Sources
- (1) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6122405/ [2018 Sep; 16(3): 1597–1602. Published online 2018 Jul 6]
- (2) The Safety and Anti-Tumor Effects of Ozonated Water in Vivo.
Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Oct 22; 16(10):25108-20.
- (3) Ozone Therapy for Tumor Oxygenation: a Pilot Study. Clavo B, Pérez JL, López L, Suárez G, Lloret M, Rodríguez V, Macías D, Santana M, Hernández MA, Martín Oliva R, Robaina F. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2004 Jun 1; 1(1):93-98.





