Ozone Therapy as a treatment for acute bacterial infection
Ozone Therapy as a primary and sole treatment for acute bacterial infection: Case Report
Medical Gas Research
Keywords: Ozone Therapy, infection, antimicrobial,cellulitis, antibiotic resistance, immune modulation, oxygenation, reactive oxygen species
Abstract
“This report presents background basic ozone science and a case report of acute bacterial infection – tick bite cellulitis, which immediately responded to ozone therapy as the sole treatment, and which fully resolved within 24-48 hours. Ozone therapy could be considered as an adjunctive or alternative therapy for bacterial infection.” (1)
Introduction
“The antibiotic resistance crisis has been attributed to the overuse and misuse of these medications, as well as a lack of new drug development by the pharmaceutical industry due to reduced economic incentives and challenging regulatory requirements.” Harvard scientists have graphically shown in a cinema how fast bacteria will naturally become resistant to antibiotics and simply grow right into the drug laced medium given a short period of time.
Ozone (O3) is an allotrope of oxygen. It is the strongest naturally occurring oxidant. It is produced in nature by lightning and ultraviolet irradiation. Ozone can be created similarly with a corona high arc discharge.” (1)
“A succinct summary of ozone history and use can be found in the review by Elvis and Elka. Nikola Tesla patented (U.S. Patent Number 568177) the first commercial ozone generator. Medical ozone is made by passing medical grade oxygen through the discharge. This creates a gas mixture of 1-5{e43154ce913794517af217fcab284b44cfe906ba9a1c4ba2ecde5a9be0395ec5} ozone and 95-99{e43154ce913794517af217fcab284b44cfe906ba9a1c4ba2ecde5a9be0395ec5} oxygen, which is the “ozone” used for treatment. Germans doctors in the trenches used ozone to disinfect wounds during World War I. German doctors expanded the world of ozone by introducing ozone treat blood, either by direct gas administration or removing 50-200 mL blood, ozonating it, and returning it.
Basic research from Italy (Bocci)(2) and Cuba (Menendez)(3) has led to publication of books containing their published studies. Both researchers have independently confirmed: 1) immune system modulation balancing its inflammatory/anti-inflammatory cytokines, 2) increase in production of red blood cell (RBC) 2,3 diglycerophosphate (DGP) (greater oxygen release), and improved rheology properties of blood (increased RBC flexibility) 3) elevation of key anti-oxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), and increased glutathione, achieving a redox cell balance.” (1)
“Ozone is directly germicidal, kills 99{e43154ce913794517af217fcab284b44cfe906ba9a1c4ba2ecde5a9be0395ec5} of bacteria in a few seconds and is 100× more effective at destroying bacteria than bleach.Ozone, bleach and hydrogen peroxide have been used for generations as germicides, without any development of resistance. It has been known for decades that our body produces abundant oxidants to hurl at invading pathogens, such as hydrogen peroxide, superoxide,(4) hypochlorite, and singlet oxygen. Recently, Scripps reported a revolutionary discovery that our bodies actually generate ozone as part of its oxidative armamentarium in fighting infection.(1)
“A very common form of ozone administration worldwide is direct application of intravenous gas (personal knowledge). Intravenous oxygen has been administered for decades as a treatment in Europe. It has been shown to provide powerful immunological effects, improve blood rheology and oxygenation,and even increase the important prostacyclin/thromboxane ratio.(5)The most accepted form of ozone administration is “major auto hemotherapy”. This administration is accomplished by removing an aliquot of blood, heparinating it, then adding oxygen/ozone gas, mixing, and returning it under gravity. This method has been improved with newer technology in a procedure called “hyperbaric ozone therapy” (HBO3). In this method, the blood, generally 200 mL, is withdrawn into a vacuum glass bottle and heparinated. Oxygen/ozone gas, at 30-70 μg ozone/mL, is pumped into the bottle under pressure, up to 2 atmospheres absolute (ATA, 2.066 kg/cm2). This constitutes a single pass. The method, developed by German physician Horst Kief,(6) provides for better mixing of the gas and blood, more rapid execution and delivery of the treatment and additional beneficial effects of dissolved oxygen gas.
Finally, bacterial infections have recently been noted to take on an ominous dimension – biofilms, virtually impossible to conventionally treat.(7) Ozone gas is known to quickly cut through and destroy biofilms.(8) This property suggests activity by ozone against resilient biofilm establishes microbial communities, where antibiotics generally fail.” (1)
Case Report
A 56 year old male presented with an acute right thigh cellulitis from a tick bite which occurred 1-2 days before. At presentation he was afebrile, but with a rapidly spreading rash on his upper leg (Figure 1).
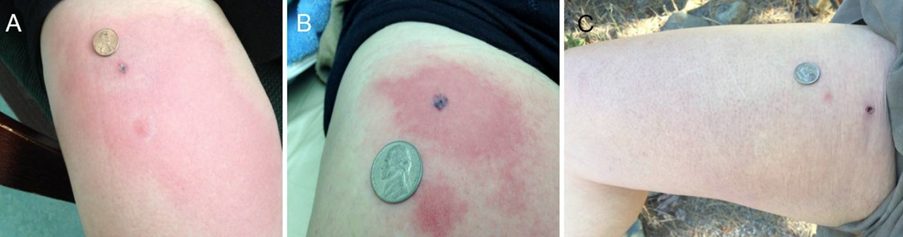
The patient was a long-term patient of the clinic. He had received ozone from us 3 years before for Lyme disease (without antibiotics), and fully recovered. He was offered antibiotics to take immediately for medical-legal reasons but refused due to his past success with ozone therapy. He did depart with a written prescription upon demand. He received ozone therapy by the hyperbaric method described above, receiving 144,000 μg over one hour at an average pressure of 1.9 ATA. He returned the following photograph two days later reporting that he made good on his decision not to take antibiotics. The rash began disappearing the following day and disappeared on the second day.
Discussion and Acknowledgements
Sources
- Med Gas Res. 2018 Jul-Sep; 8(3): 121–124. Published online 2018 Sep 25. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.241078
- (2) Bocci: Ozone A new medical drug: Springer; 2011- Netherands.- Google Scholar
- (3) Menendez S, Weiser M. Havana, Cuba: 2016. Advances of Ozone Therapy in Medicine and Dentistry –https://scholar.google.com
- (4) Babior BM. The respiratory burst of phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1984;73:599–601. [Google Scholar]
- (5) Stichtenoth DO, Kreutzer FJ, Gutzki FM, Tsikas D, Nowak V, Frölich JC. Effects of intravenous oxygen on prostacyclin and thromboxane formation in patients with peripheral occlusive arterial disease. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2001;65:211–214. [Google Scholar]
- (6) Kief H. Private Communication. 6 Private Communication 2016. [Google Scholar]
- (7) Bjarnsholt T. The role of bacterial biofilms in chronic infections. APMIS Suppl. 2013:1–51. [Google Scholar]
- (8) Bialoszewski D, Pietruczuk-Padzik A, Kalicinska A, et al. Activity of ozonated water and ozone against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Med Sci Monit. 2011;17:BR339–344.[Google Scholar]