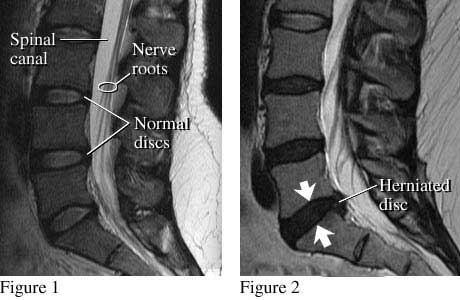
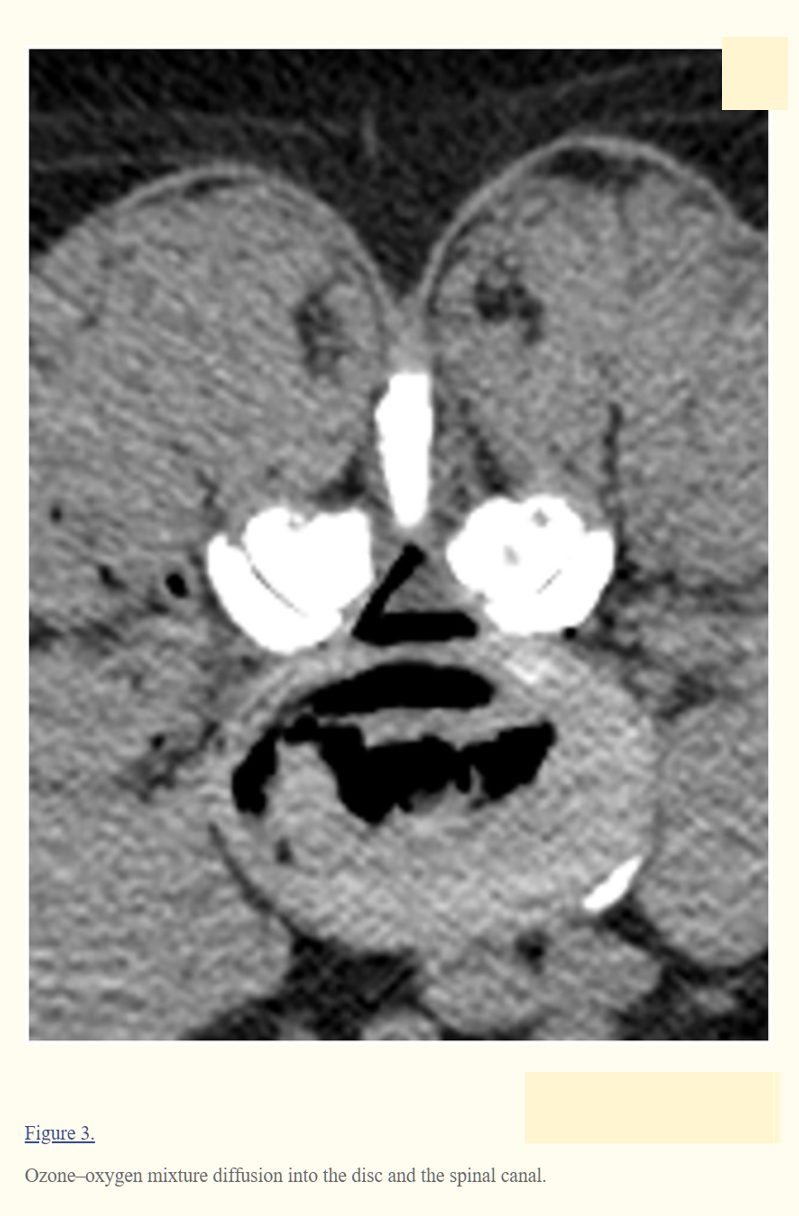
Treating lumbar disk herniation by oxygen-ozone therapy
Rational approach, technique and selection criteria treating lumbar disk herniations by oxygen-ozone therapy
Interventional Neuroradiology
Keywords: Lumbar pain, herniated disk, oxygen-ozone therapy, fluro- and CT-guidance, selection criteria.
(Treating lumbar disk herniation by oxygen-ozone therapy )
Abstract
“Radicular lumbar back pain is an important public health problem not yet benefiting from a unequivocal treatment approach. Medical and physical therapies represent the first solution; however, when these fail, the second therapeutic step is still controversial and mini-invasive treatments may play an important role. In these cases oxygen–ozone therapy has been proved to be a very safe and effective option that is widely used with different modalities. This paper, by reviewing oxygen–ozone therapy literature data, aims to describe the rationale of oxygen–ozone therapy for the treatment of lumbar disk herniations, propose an effective procedural technique and clarify patient selection criteria; furthermore, complications and follow-up management are also considered.” (1)
“Ozone (O3) is a strongly oxidant gas with antiseptic, immunomodulating, analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. Oxygen–ozone gas mixture (O2O3) is commonly used in clinical practice, mostly in Europe and Asia, in the treatment of nociceptive-neuropathic pain, in inflammatory and degenerative processes of the muscle-skeletal system and especially in degenerative disc disease and disc herniation. O3 is administered in the form of O2O3 at non-toxic concentrations ranging from 1 µg to 40 µg of O3 per ml of oxygen, using various percutaneous methods.
The biological action of medical ozone is not fully understood but some mechanisms of action have been proposed to explain its efficacy in disc herniation treatment:
-
Reduction of the inflammatory components. O3 interrupts the self sustained cycle of the inflammatory cascade by altering the breakdown of arachidonic acid to inflammatory prostaglandins.
-
Hyper-oxygenation of the area of interest. Disc herniation impinges on the venous and arterial flow, causing phlebostasis and arteriostenosis, which lead to hypoxemia of the tissues; by applying O2O3 to the herniated site, oxygen concentration increases.
-
Diminishing the size of the herniation. O3 breaks down the glycosaminoglycans chains in the nucleus pulposus and reduces their ability to hold water, thereby shrinking the nucleus and subsequently reducing intradiscal and peri-radicular pressure.
-
Stimulation of the repair process. O3 promotes the fibroblastic activity, inducing collagen deposition.”(1)
Click here for Procedural Technique
(Treating lumbar disk herniation by oxygen-ozone therapy)
Conclusions
“O2O3 therapy is a safe and cost-effective approach for patients with sciatica refractive to conservative therapy, having demonstrated good short- and long-term results, significantly shorter recovery time compared with the alternative treatments,10 and reduction of the need for surgery. Moreover, it must be considered also that patients without a good response to O2O3 therapy may still undergo surgical discectomy.” (1)
Sources
- (1) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5564357/ Interventional Neuroradiology- 2016 Dec; 22(6): 736–740. Published online 2016 Aug 2.
- Mario Muto,1 Francesco Giurazza,
 1,2 Ricardo Pimentel Silva,3 and Gianluigi Guarnieri1
1,2 Ricardo Pimentel Silva,3 and Gianluigi Guarnieri1